The Earth rotates about an imaginary line that passes through the north and south poles of the planet.
This imaginary line is called the axis of rotation and ALWAYS points in the same direction
The North Pole always points toward the star Polaris, commonly called the North Star
Think of the Earth as a spinning top, that is tipped to one side, at an angle of 23.45 degrees. The tilt of the Earth and the Earth’s orbit work together to create the seasons.
The axis of rotation and the North Star (Polaris). The Earth’s tilt on its axis leads to one hemisphere facing the Sun more than the other hemisphere and gives rise to seasons.
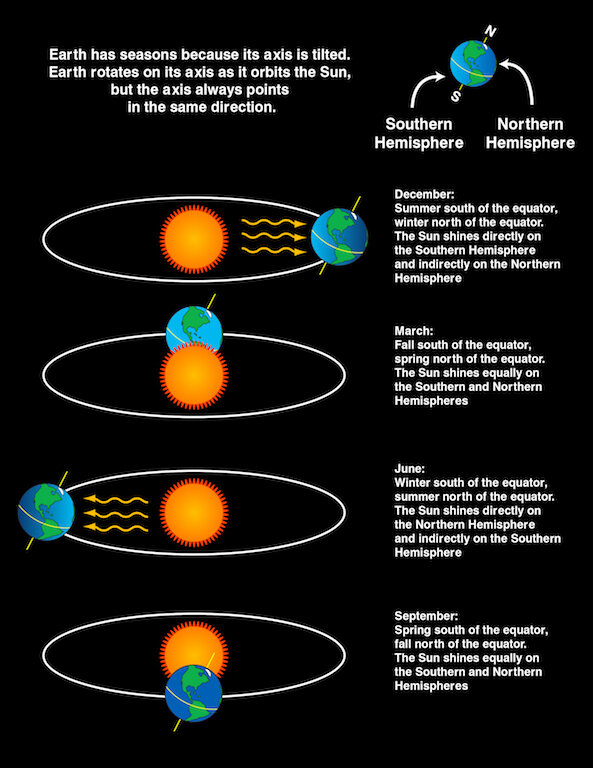
The Tilt of The Earth: The Sun & The Seasons
As the Earth travels around the Sun, it remains tipped in the same direction toward the North Star. When the northern half (Northern Hemisphere) of the Earth is pointing towards the Sun (summer), the southern half (Southern Hemisphere) is tilted away from it (winter).
Notice that when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, the Southern Hemisphere is tilted away from it, and explains why the hemispheres have opposite seasons.
Image Source: Wikimedia Commons
Southern Hemisphere Summer
The summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere happens on December 21st or 22nd. This is the day that the tilt of the Earth’s axis, maximally points toward the Sun in the Southern Hemisphere.
When it’s the summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere, it’s the winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere
The Sun’s rays more directly strike the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere during summer
Summer Solstice in the Southern Hemisphere
Notice the rays from the Sun striking the Tropic of Capricorn more directly in the Southern Hemisphere summer?? Also, notice the southern hemisphere tilting towards the Sun, leaving the Northern Hemisphere in winter. (Figure 2)
Southern Hemisphere Winter
The winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere happens on June 21st or 22nd. This is the day the Earth has maximally tilted away from the Sun in the Southern Hemisphere.
In the Northern Hemisphere, the North Pole is tilted towards the Sun, with the Sun’s rays striking the northern half more directly in the northern summer.
Winter Solstice in the Southern Hemisphere
Notice how the Earth’s axis is tilted toward the sun in the northern half, which leaves the southern hemisphere in winter? (figure 3)
Is there a North Star equivalent in the Southern Hemisphere?
There is no true equivalent. Sigma Octantis, based on position, could be considered the “South Pole Star,” however, unlike Polaris (North Star) it’s too dim to be used as a consistent celestial reference point.
Sigma Octantis is also over a degree away from the true south pole
Jesse is Director of Pedal Chile and lives in La Patagonia (southern hemisphere). Jesse has a Master of Science in Health & Human Performance and a Bachelor of Science in Kinesiology. Hobbies: Mountain biking, snowboarding, reading, taster of craft beers, researcher, & star-gazer.
Sources :
Duro/ESO, A. “English: Science and Art Unite in This Beautiful Photograph, Taken in Chile’s Atacama Desert by ESO Photo Ambassador Adhemar M. Duro Jr. To Create This Visual Masterpiece Adhemar Pointed His Camera at the Sky’s South Pole, the Point at the Centre of All the Bright Arcs and Circles. All the Stars in the Night Sky Revolve around This Point. Over a Period of Several Hours, This Motion Creates Star Trails, with Each Individual Star Tracing out a Circle on the Sky. These Trails Display the Various Brightnesses and Colours of Each Star, Creating a Captivating Scene! Towards the Top Left of the Image, You Can See a Short, Bright Streak of Light Cutting across the Trails — This Is Caused by a Meteor, Burning up in a Flash of Light as It Enters Earth’s Atmosphere. The Desert’s Harsh and Arid Landscape, Illuminated Here by the Light from the Stars….” Wikimedia Commons, 1 Aug. 2016, commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:All_In_A_Spin_Star_trail.jpg. (Figure 1)
“File:Earth-Lighting-Summer-Solstice EN.png - Wikimedia Commons.” Commons.wikimedia.org, commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Earth-lighting-summer-solstice_EN.png. (Figure 3).
“File:Earth-Lighting-Winter-Solstice EN.png - Wikimedia Commons.” Commons.wikimedia.org, commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Earth-lighting-winter-solstice_EN.png. (Figure 2).
Shaw, Justin. “Justin Shaw, Beaverton, Oregon. “Is there an equivalent to the North Star in the Southern Hemisphere?” Astronomy.com, 26 May 2009.
“What Causes the Seasons? | NASA Space Place – NASA Science for Kids.” Nasa.gov, 2016, spaceplace.nasa.gov/seasons/en/.
“Why Does Earth Have Seasons? | NOAA SciJinks – All about Weather.” Scijinks.gov, scijinks.gov/earths-seasons/.